Dark matter is a very mysterious matter in the universe. Unlike ordinary matter, we cannot see dark matter, and dark matter will not interfere with ordinary matter.
Although dark matter does not interfere with ordinary matter, dark matter also has a gravitational effect, so it can interfere with the motion, light, magnetic field, etc. of celestial bodies. By observing the motion patterns of spiral galaxies in the universe, observing the structure of the universe through gravitational lenses, we can judge dark matter and darkness. Energy occupies more than 96% of the mass of the universe.
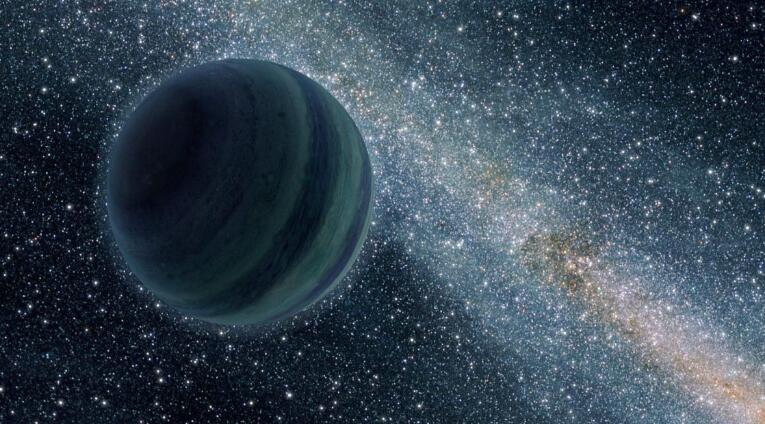
There may be high-density dark matter inside gaseous planets?
Although dark matter cannot be directly observed, scientists know that dark matter is still subject to gravity.
In the universe, all kinds of celestial bodies attract dark matter to gather, but since dark matter cannot be seen, scientists cannot observe dark matter well and understand the characteristics of dark matter.
The James Webb Space Telescope, which will be launched in the future, will give scientists a new way of observation-the dark matter research team proposes to use a new space telescope to observe gaseous planets in the universe. The larger the mass of gaseous planets, the easier it is to accumulate. Dark matter, and dark matter in gaseous planets, are more likely to collide with each other, which in turn produces additional thermal effects.
At present, most theories believe that dark matter is a kind of mysterious particles, and these particles basically do not interact with conventional particles, but dark matter particles can collide and annihilate and generate energy.
If scientists’ guesses about dark matter are correct, then in the universe, dark matter will gather around large celestial bodies, or even crash into celestial bodies, and accumulate inside celestial bodies.
Compared with other planets, gaseous planets are easier to accumulate dark matter inside, and it is also easier to observe. Scientists can use astronomical telescopes to observe the thermal signals of these gaseous planets and look for abnormal energy changes.
According to the dark matter research team’s plan, outside the solar system, it is the best choice to look for gaseous planets larger than Jupiter, especially gaseous planets far away from stars.
According to scientists’ calculations, the density of dark matter inside gaseous planets larger than Jupiter can reach more than six times that of the outside world, which will greatly increase the possibility of dark matter particles colliding with each other.
The temperature of gaseous planets far away from the stars should be relatively low. If there is a special thermal signal reaction inside the planet, it means that there may be a large amount of dark matter inside the planet. Moreover, according to current astronomical scientific theories, a gaseous planet far away from the star has an abnormal temperature rise, and the only explanation is the impact of dark matter particles.
Super black holes, perhaps can make dark matter into an observable state?
Since dark matter can be affected by gravity, the area where dark matter is most dense should be near the black hole.
Since scientists predict that dark matter is a microscopic particle with a weak force, in order to gather dark matter in the universe, a black hole needs to have an unusually large mass to be able to generate enough gravity.
The largest black hole currently observed by scientists is about 66 billion times the mass of the sun, and a black hole that can accumulate a large amount of dark matter and form a dark matter ring around requires at least 100 billion times the mass of the sun.
Although black holes may accumulate large amounts of dark matter and directly form dense dark matter rings, scientists currently know very little about black holes.
According to the current physical theory, a black hole is almost an eternal celestial body, and no one knows whether a black hole has a limit, and whether a black hole of 100 billion times can appear is also an uncertain matter.
If scientists can find a super black hole that is 100 billion times the mass of the sun, dark matter will gather in large numbers near the black hole, collide with each other, and produce extremely powerful gamma rays. Scientists may be able to directly observe various phenomena of dark matter.
to sum up:
Dark matter and dark energy are just a general term for scientists’ unknown things in the universe. In fact, dark matter and dark energy may be far more than one kind of particles.
The Webb Telescope, which is expected to be launched in October, will search for gaseous planets above Jupiter’s mass in the Milky Way, and will conduct thermal imaging of these planets.
The dark matter research team believes that from the beginning of the work of the Webb Astronomical Telescope, it only takes about 4-5 years to find suitable gaseous planets and draw the planet’s thermal characteristics. Scientists will prove for the first time that dark matter may really exist!