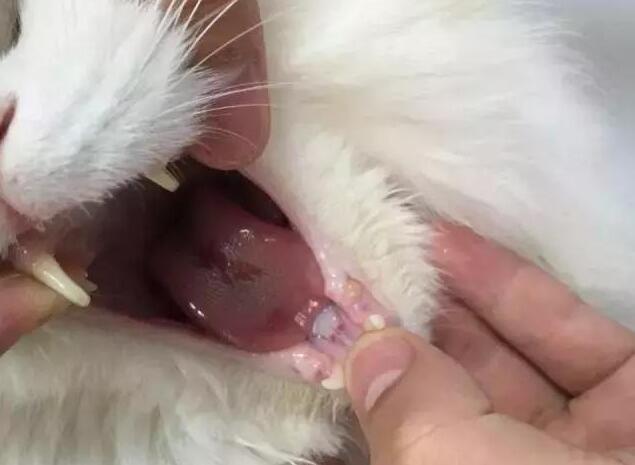
Causes of cats’ oral ulcers
The etiology of oral inflammation is quite complex, and a variety of reasons can cause oral inflammation. Various causes: mechanical injuries, such as bone spurs, fish bones, burns.
(1) Malnutrition: Vitamin deficiency can directly cause oral diseases, especially vitamin B deficiency can cause the severity of the disease. Nutritional deficiencies, such as vitamin B deficiency.
(2) Oral trauma: cats accidentally eat sawdust, iron wire, fish hooks, burrs, sewing needles and other foreign objects that puncture the mouth, causing oral inflammation or ulcers;
In addition, accidentally ingested or accidentally given heavy metals and irritating drugs, cats accidentally bite charged wires can directly cause corrosive inflammation and burn inflammation of the oral cavity. Corrosion of chemicals.
(3) Low immunity: Clostridium and spirochetes, which are part of the normal oral microorganisms, can cause necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis and stomatitis.
Bacterial viral infections, such as fusiformis, Candida albicans, feline rhinotracheitis virus, calicivirus.
(4) Diseases: viral rhinotracheitis, calicivirus, leukemia, diabetes, kidney disease, chronic gastritis, gastric ulcer, pemphigus, systemic lupus erythematosus, hypothyroidism and hypoparathyroidism, etc.
(5) Systemic diseases: Certain systemic diseases, such as anemia, can also cause cat stomatitis.
Symptoms of cats having oral ulcers
Cats suffering from feline stomatitis have reduced or annulled appetite to varying degrees, a lack of energy, a large amount of salivation in the mouth, and a string of saliva flows out of the mouth for a long time, forming a “small pool” where the cat sits and sleeps, which has a foul smell.
The oral mucosa is congested and swollen, and the sick cat resists when checking the mouth. Ulcerative glossitis damage is more common on the edge of the tongue, shaped like a half moon or horseshoe, and sometimes bleeding. Affected cats like to be near water, but do not drink. Severely ill cats may show dehydration.
When suffering from eosinophilic granuloma, small round spots that gradually increase at the edge of the lips form at first, and sometimes spread to the lips, causing the lips to become spoon-shaped, with a brown, dry appearance. Because the cat constantly licks and washes the skin, the lip lesions spread to the inner thighs, abdomen, etc.
Cat Stomatitis
Stomatitis refers to inflammation of the cat’s mouth mucosa, tongue and gums, and causes ulcers, necrosis, and secondary infections. It is characterized by oral mucosal inflammation, ulcers, pain, inability to chew and excessive salivation. Stomatitis will develop into eosinophilic granuloma if it is not treated in time.
Stomatitis can be caused by trauma, irritants, bacterial infections that accompany gingivitis, and viral infections.
The current treatments for stomatitis include medication and tooth extraction. Drug treatment is mainly based on chlorhexidine cleaning, antibiotics and hormone therapy. According to the severity of stomatitis, it can be divided into short-term treatment and long-term treatment. In short-term treatment, the use of hormones is the most effective, such as methylprednisolone and prednisolone. In long-term treatment, due to the diverse clinical manifestations, there is no most effective method among various treatment methods.
Removal of premolars and molars is an effective treatment for most refractory stomatitis. More than 80% of cats can improve their quality of life (some cats require full tooth extraction). Many owners worry that cats will have difficulty eating after tooth extraction? According to the results of clinical statistics, almost 90% of cats with full mouth extraction can eat normally (owners are better to soak cat food or give cats a soft food such as canned food. optimal).
Glossitis
The etiology is the same as that of stomatitis, that is, the mechanical action of foreign bodies (bone fragments, needles, sharpened teeth and tartar, etc.), the exposure and removal of new teeth, scalds that occur when ingesting soup, food and beverages, and chemical substances ( Glossitis can be caused by the corrosion of toxic agents such as iodine and mercury, and infections such as herpes virus.
According to statistics, cats younger than 1 year old are prone to ulcerative glossitis. Sick cats refuse to eat, are depressed, and cannot drink water in severe cases, so they have symptoms of dehydration. From the corners of the mouth, there is often a thick, foul-smelling saliva with pus and blood. Severe pain occurred and oral examination was refused. Swelling and fever of the submandibular lymph nodes are sometimes seen. Dermatitis is caused by saliva flowing from the head and neck to the forelimbs.
Viral infection
Among the viral infections that easily induce stomatitis or glossitis, there are HIV infections that are not transmitted to humans but do not have vaccination or treatment methods. Leukemia virus infections that rarely occur but have a poor prognosis once they occur are viral and present symptoms of nasal cold. Rhinotracheitis and so on. This is also the safest and most effective way to prevent this disease. In addition, if the flu virus is infected, blisters and ulcers will appear on the surface of the tongue, accompanied by severe pain, so that you can’t even drink water. However, this infection can also be prevented by vaccines, so it must be vaccinated.