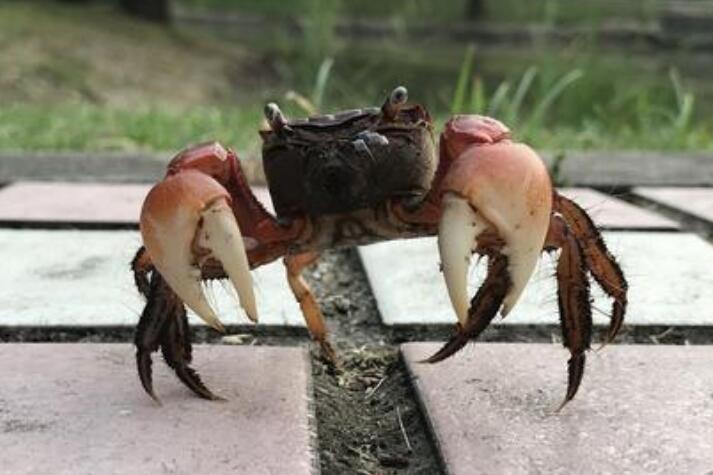
The reason why the crab is walking sideways
From the perspective of scientific popularization, crab is an ancient migratory animal. Its inner ear has directional small magnets and is very sensitive to geomagnetism. As the earth’s geomagnetic north and south poles have been reversed many times over the long years, the small magnets in the crabs have lost their original orientation. In order to survive the reversal of the earth’s magnetic field, the crab adopts the approach of “responding to all changes with the same”, and simply does not advance or retreat, but walks sideways.
From the perspective of physiological structure, each foot of a crab is composed of seven joints, and the joints can only move up and down, just like a person’s elbows cannot be turned outwards and knees cannot be bent backwards. In fact, crabs can walk forward slowly, but their stride, speed and efficiency are far lower than walking horizontally. To verify this is very simple, you can grab a crab and shake it lightly, and its eight legs will tremble left and right, but if you hold its legs back and forth, the shaking will be small, and then it will be very hard. It might be cut off with a “pop”.
On the other hand, the crab’s chest is wider than the front and rear, and the eight legs stretch on both sides of the body. Its forefoot joints can only bend downwards. These structural features also make the crab can only walk sideways.
How the crab moves
Geomagnetic field theory
Crabs rely on the geomagnetic field to determine the direction. In the long years since the formation of the earth, the north and south poles of the geomagnetic field have been reversed many times. The reversal of the earth’s magnetic poles makes many creatures at a loss what to do and even causes extinction. Crab is an ancient migratory animal. Its inner ear has directional small magnets and is very sensitive to geomagnetism. Due to the reversal of the geomagnetic field, the small magnet in the crab loses its original orientation. In order to survive the reversal of the earth’s magnetic field, the crab adopts the approach of “responding to all changes with the same”, and simply does not advance or retreat, but walks sideways.
Biological perspective
The head and breast of a crab are indistinguishable from each other in appearance, so they are called cephalothorax. The full feet of this animal grow on both sides of the body. The first pair of chelated feet is not only a tool for digging holes, but also a weapon for defense and offense. The remaining four pairs are used for walking and are called walking feet. Each foot is composed of seven sections, and the joints can only move up and down. The width of the chest of most crab heads is greater than the length, so when crawling, only one foot can bend, grab the ground with the toe, and the other foot stretches out. When the toe reaches the ground, it begins to shrink. The bent foot straightened out immediately, pushing the body to the opposite side. Because the lengths of these pairs of feet are different, the crab actually moves sideways and forwards. However, not all crabs can only rampage. For example, long-armed monk crabs living in groups on the beach can run forward. Many spider crabs living in the seaweed can also climb vertically on the seaweed.
It was found
Through experiments, it is found that the bone eyes (where the muscle bundle passes) in the crab body are connected to each limb. There are two upper and lower bone eyes (ie, two muscles) connected to each limb. Moreover, the bending direction of the joints at the base of the limbs is the dorso-abdominal direction, so when the muscles contract, the limbs are moved in the dorsal-abdominal direction, so the crab moves laterally.